Conveyor belts are an integral component of food manufacturing operations, facilitating the efficient transportation of food products through various processing stages.
While the proper use of conveyor belts can significantly increase productivity, it is crucial to prioritise safety measures to protect both employees and the integrity of the food products. Implementing safety measures for conveyor belts not only prevents accidents and ensures worker safety but also maintains compliance with stringent food safety standards.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore crucial safety measures for conveyor belts in food manufacturing, ranging from design and installation to operator training and maintenance procedures. Furthermore, we will discuss the importance of adhering to safety standards and best practices, such as the Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association (CEMA) guidelines, to create a safe, efficient, and compliant food manufacturing environment.
Key Conveyor Belt Safety Measures in Food Manufacturing
Design and Installation Considerations
To ensure safety in food manufacturing operations, it’s essential to pay attention to the design and installation of conveyor belt systems. Key considerations include:
1. Proper Layout Design: When designing the layout of your conveyor belt system, consider factors such as ergonomics, clearances, and aisle widths to facilitate safe movement and working conditions for employees.
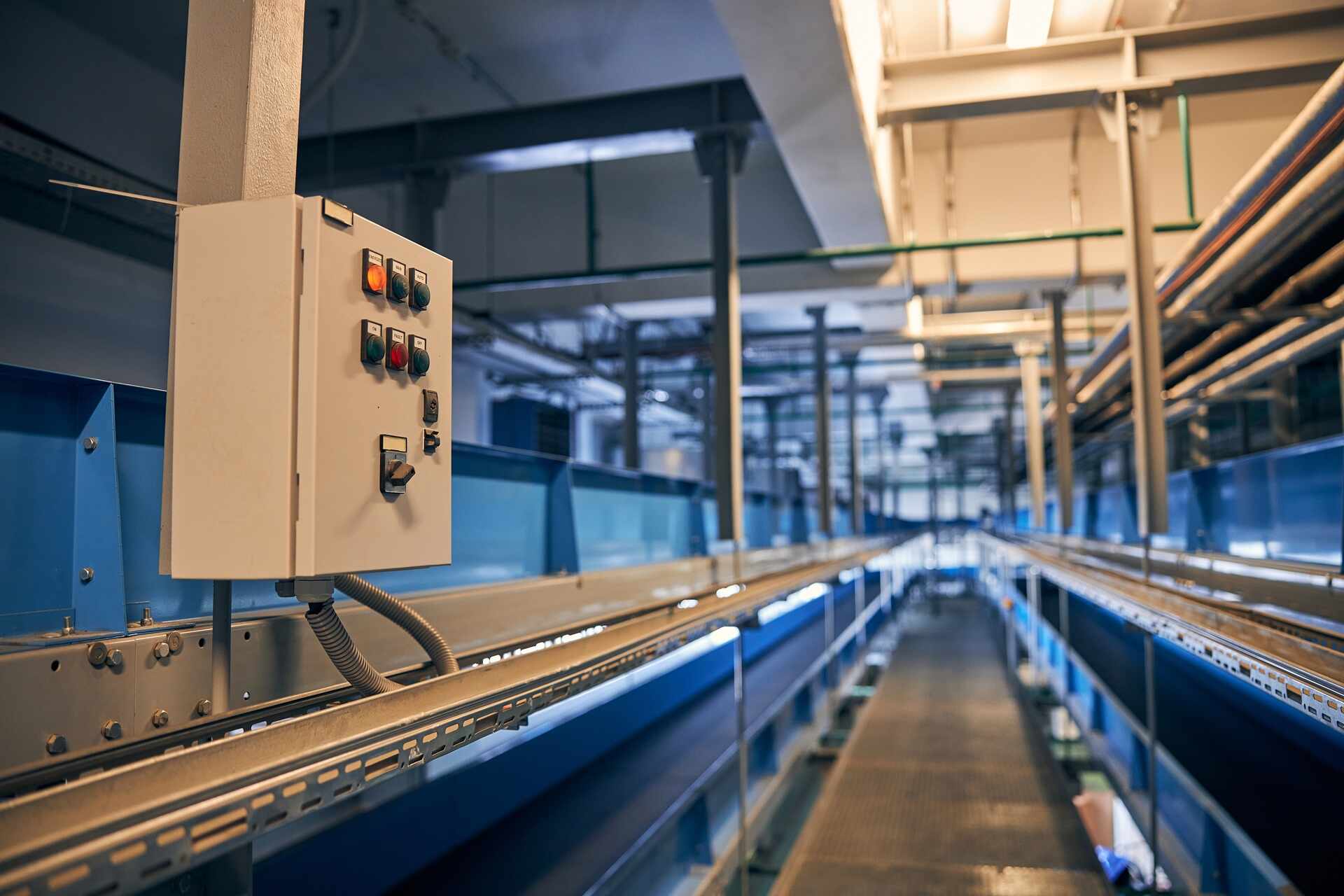
2. Guarding: Conveyor belt systems should include appropriate guarding to protect workers from potential hazards, such as moving parts or pinch points. According to CEMA guidelines, guards should be secured and designed to prevent accidental removal, ensuring the safety of personnel during operation and maintenance.
3. Emergency Stop Devices: Install conspicuous emergency stop devices along the conveyor belt system to allow for prompt shutdown in hazardous situations. Regularly inspect and test these devices to ensure their effectiveness.
4. Proper Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting around conveyor belts to facilitate visibility, reduce eye strain, and minimise the risk of accidents.
Operator Training and Procedures
Comprehensive operator training is essential to ensure safety when working with conveyor belt systems. Key training elements include:
1. Safe Operating Procedures: Train employees on established safe operating procedures for the conveyor belt system, including start-up and shutdown processes, correct loading of products, and proper use of safety devices.
2. Hazard Identification and Response: Provide training to help employees identify potential hazards, such as loose clothing or improperly loaded products, and teach appropriate responses to critical situations.
3. Emergency Response Procedures: Train employees on the proper use of emergency stop devices and ensure they are familiar with necessary emergency response protocols, such as evacuating the area or locating first aid equipment.
4. Ongoing Training and Refresher Courses: Regularly provide refresher training sessions and require employees to participate in ongoing safety education to maintain their knowledge of safe operating procedures and stay up-to-date with any changes in safety standards.
Routine Inspections and Maintenance
Conducting routine inspections and maintenance of conveyor belt systems is crucial for ensuring continued safe operations and minimising the risk of accidents.
1. Visual Inspections: Regularly inspect conveyor belts for signs of excessive wear, potential hazards, or damage that could compromise safety. Visually examine the belt and components, such as rollers, idlers, and pulleys, for misalignment or damage.
2. Mechanical Inspections: Conduct systematic mechanical inspections of conveyor belt systems to assess the integrity of components, including chains, sprockets, drives, and bearings.
3. Proper Maintenance Practices: Implement proper maintenance practices, including prompt repairs or replacement of damaged components and regular cleaning to maintain conveyor belt hygiene and reduce the risk of product contamination.
4. Recordkeeping and Documentation: Maintain accurate records of inspection and maintenance activities, as well as any identified issues and their resolution. This can help streamline future inspections and provide crucial information in the event of a safety audit or incident investigation.
Compliance with Safety Standards
To ensure a safe food manufacturing environment, it’s essential to adhere to relevant safety standards and guidelines for conveyor belt systems.
1. CEMA Guidelines: Follow the guidelines provided by the Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association (CEMA) for the design, construction, and operation of conveyor belt systems to ensure safety and prevent accidents.
2. Machine Safety Directives: Adhere to regional machine safety directives, such as the Machinery Directive in the European Union, to maintain compliance with legal requirements and uphold the highest standards of safe operation.
3. Food Safety Regulations: Ensure that your conveyor belt system complies with applicable food safety regulations and guidelines, such as Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) principles, to protect the integrity of food products and ensure safety along the production line.
Final Thoughts
Implementing safety measures for conveyor belts is crucial for maintaining a safe, efficient, and compliant food manufacturing environment. By focusing on factors such as proper design and installation, training and procedures, routine inspections and maintenance, and compliance with standards, food manufacturers can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and achieve a higher level of efficiency and productivity.
Partnering with a trusted conveyor belt solutions provider, such as Change Parts, can help ensure that your conveyor belt system adheres to the relevant safety measures and contributes to a safe and successful food manufacturing operation.
Contact our team today to discover our tailored conveyor belt solutions, exceptional products, and comprehensive support that enhance the safety and efficiency of your food manufacturing operation.